Incorporating Acoustics into Corporate STEM Spaces
What to Consider Acoustically Within These Spaces | November 15, 2024
In the constantly changing landscape of corporate STEM facilities, acoustics play a critical role. As organizations work to create environments that encourage innovation and collaboration, managing sound is becoming increasingly important.
What Happens When the Acoustics are Poor?
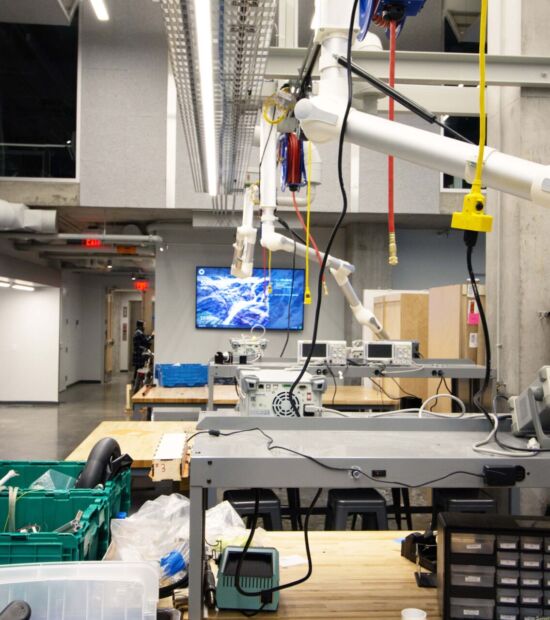
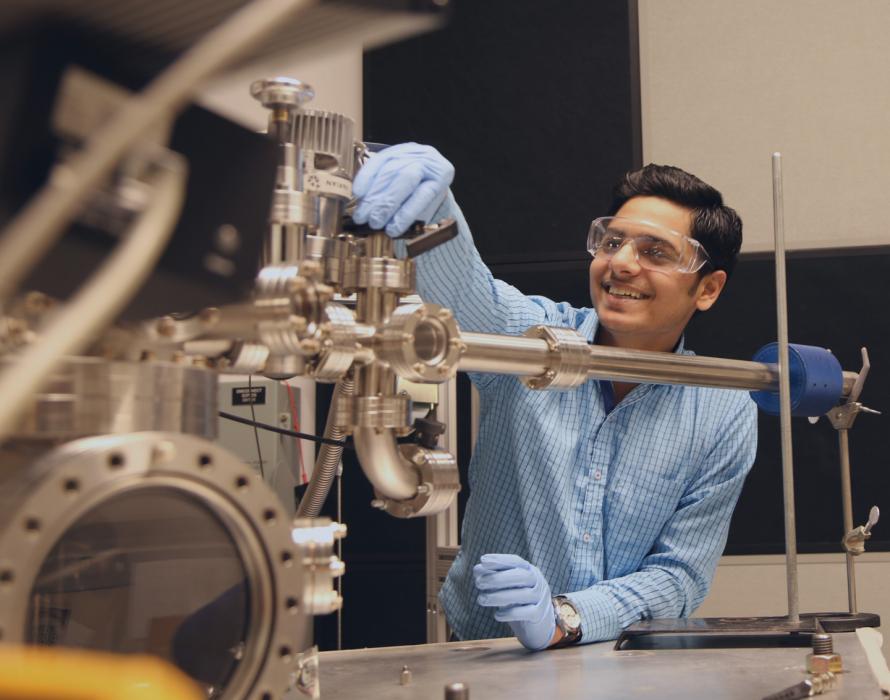
This can lead to decreased productivity, hindered communication, and a compromised work environment. Certain scientific and medical research equipment, like microscopes and imaging devices, need to be carefully placed within the facility to account for areas that require less excess noise.
How Can This be Fixed?
Excess noise can be abated by locating the sources in areas where external vibrations can be minimized. This could be within a basement level or a lower level that is optimized for sound isolation. Vibrations from these machines can interfere with ongoing research and testing, so location is imperative in laboratory design.
Beyond vibration control, the auditory environment in a research facility can significantly impact researchers’ ability to focus and perform their work effectively. Sound is able to travel through certain types of building materials & it is important to take this into account in the early stages of planning.
Laboratories Require Different Solutions
Different types of laboratories require unique design and construction, this is what the acoustician uses as a starting point to determine best practices for the facility. Sound-absorbing materials in walls and ceiling designs can help to reduce sound reflection and reverberation. If the space allows, acoustic paneling, carpet, and specially designed ceiling tiles all contribute to a quieter environment.
Achieving structural vibration limits requires close coordination between the acoustic consultant, architect, structural engineers, and MEP engineers.
Strategically zoned areas within the facility is another technique for separating noise from lab activities from quieter research-focused spaces. Research & testing labs often house equipment that generate large amounts of noise, including exhaust fans, fume hoods, and cooling equipment.
Taking the equipment into account, sound isolation techniques are brought into the mix. Soundproofing doorways, using naturally sound absorbing building materials, and installing double-glazed windows can help contain the noise to the area where it is being produced.
Consider External Systems
Necessary mechanical systems can also act as a significant source of noise. Seeking out quieter HVAC systems and installing sound-absorbing ductwork can help to reduce ongoing noise.
Labs for robotics research, computer engineering, and imaging research often have strict vibration tolerances that need to be met to achieve accurate results. Achieving structural vibration limits requires close coordination between the acoustic consultant, architect, structural engineers, and the MEP.
Noise Management in STEM Facilities
Aside from a contained laboratory environment, it’s also important to contain noise that might spill over from one lab to another, or to neighboring offices and common areas. Managing noise leads to a reduction in potential distractions, as even minor interruptions in high-stakes research settings can lead to costly errors.
Benefits of the Right Acoustic Environment
The right acoustic environment can boost focus, collaboration, and productivity, which leads to heightened job satisfaction. With various research spaces within a building, each with unique occupancy needs, creative solutions are necessary to meet the client’s expectations for privacy within the facility.
Creating Innovative Environments
Integrating acoustic design principles thoughtfully into research facilities isn’t just about reducing noise, it’s about creating environments where scientists can continue to innovate and push boundaries.
As technology evolves, research methods and lab equipment will change, but acoustic design can support all current and future uses without interfering with the lab’s functionality.
In a volatile environment where high-caliber research is being completed, it’s crucial that occupants are able to clearly hear safety warnings, audible alarms, and evacuation instructions.
For more on acoustics design and consulting that BrightTree Studios offers, check out our article titled A Closer Look at BrightTree Studios’ Acoustic Offerings.